RBI Annual Report and HBIE - Data Tables
(This
is for information purposes only. This should not be construed as a
recommendation or investment advice even though the author is a CFA Charterholder. Please consult your financial
adviser before taking any investment decision. Safe to assume the author has a vested
interest in stocks / investments discussed if any.)
Reserve Bank of India (RBI), among other reports, publishes two important reports annually, namely, Annual Report and Handbook of Statistics on Indian Economy (HBIE). These two reports contain a lot of reports concerning various aspects of Indian economy and data.
Let us briefly examine what these two reports contain.
1. Annual Report
Reserve Bank of India's Annual Report is a treasure trove of information containing the record of its financial affairs of the past year. It also contains lots of data and information.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank dealing in various functions. RBI is obligated to submit the report annually to Government of India. The report is usually made public within two months from the end of the financial year, that is, by the end of May every year.
RBI's financial year (accounting year) was changed from July-June to April-March in 2021. Till financial year 2019-20, it was July to June. And from financial year 2020-21, it was changed from July-June to April-March. FY 2020-21 was the transition year.
So, FY 2020-21 was from July 2020 to March 2021 (nine months only). From FY 2021-22 onward, it is from April to March.
Year-wise annual reports can be accessed from the weblink and you can click on the year to access the specific report. Individual annual reports are available from 1998 till now. The PDF of the 337-page Annual Report 2022-23 can be accessed here.
The contents of the annual report lists out topics covered, charts, boxes and appendix tables. Let us see what the broad contents of the report are:
a) The topics covered include:
- assessment of Indian economy's prospects
- review of economy
- monetary policy operations
- credit delivery
- financial markets
- foreign exchange management
- regulation and supervision
- financial stability
- public debt management
- currency management
- payment and settlement systems
- RBI Accounts for the current financial year
b) The boxes provide analyses, among other things, on:
- various aspects of Indian economy
- inflation dynamics
- currency demand
- term and risk premia
- India exports
- monetary policy
- stressed assets and asset quality of Banks
- sovereign green bonds
c) Appendix table provide data on:
Details of tables are given below.
Some important charts and boxes in the AR 2022-23 are:
page 28 of the PDF - high frequency indicators (HFIs)
page 49 - currency demand paradox - it lists out reasons for increase in currency demand and growth in digital payments simultaneously
page 174 - sovereign green bonds or SGrBs
page 182 - Banknotes in circulation (volume-wise and value-wise data provided for denominations of Rs 2 to Rs 2,000)
page 191 - payment system indicators
page 237 - fostering of risk culture
page 261 - main functions of RBI
page 282 - Annex I - chronology of RBI's major policy announcements
Pages 300 to 309 provided data:
Appendix Table 1 - macroeconomic and financial indicators:
- real GDP growth rates
- foodgrains output
- IIP
- CPI and WPI
- bank deposits
- various interest rates, call money, G-Sec, T-bill, etc.
- liquidity: LAF, MSS, etc.
- government finances: fiscal deficit
- BoP, current account deficit (CAD)
- net capital flows
- external debt- GDP
- import cover
- short term foreign debt to reserves
- exports
- exchange rate of INR
Table 2 - Growth rates of GDP:
- GFCF or gross fixed capital formation
- exports as a % of GDP
- imports as a % of GDP
Table 3 - gross savings:
- household sector
- net financial savings
Table 3 -money, inflation, money and credit:
- CPI and WPI
- reserve money
- currency in circulation or CIC
- CD ratio
- credit to GDP ratio
Table 5 - capital market:
- public issues
- equity and debt
- private placement
- QIP
- secondary market
- Sensex / Nifty 50 levels
Table 6 - key fiscal indicators: (data from 1990 to 2024)
- primary deficit (both centre and states)
- gross fiscal deficit (both centre and states)
- outstanding liabilities
Table 7 - government finances:
Table 8 - Balance of Payments (BoP)
- current account - exports and imports
- capital account - FDI and FPI flows, ECBs, NRIs, etc.
- trade deficit as a % of GDP
- current account deficit as a % of GDP (CAD to GDP ratio)
2. HBIE
As mentioned above, another important document published by RBI annually is Handbook of Statistics on Indian Economy (HBIE). RBI on its website has provided yearly reports from 2001 to 2023.
The HBIE 2022-23 has 240 tables and the contents range from GDP growth at current and constant prices, gross value added (GVA), per capita income, agri output, money, banking, financial markets, public finances, balance of payments (BoP), current, external sector and others.
The 437-page PDF of the full document for FY 2022-23 can be accessed here. The data are provided as annual series, quarterly series, monthly series and less-than-monthly series.
The HBIE also has 'Explanatory Notes' providing details on notes to these 240 tables. The HBIE is usually released during the third week of September every year.
Some tables that may be interesting in the FY 2022-23 document are:
Table 1 to 156 below provide annual series data:
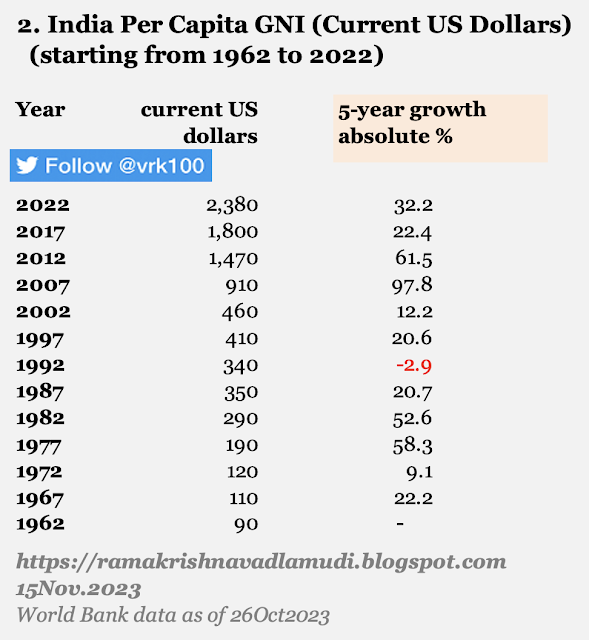
Tables 1 and 2 of the PDF - (at current and constant prices) macro-economic indicators, like, population, GVA, net taxes, GDP, savings, per capita GDP and others
Table 12 - changes in financial savings and liabilities of households (more than 40 years data)
Table 15 - index numbers of agri area, output and yield (30 years data)
Table 17 - agri output - foodgrains (almost 60 years data)
Table 21 - foodgrains yield
Table 25 - MSP for foodgrains (more than 30 years data)
Table 34 - production and imports of crude oil (35 years data)
Tables 37 & 38 - WPI and CPI (50 years data)
Table 39 - average price of gold & silver (domestic and foreign prices) (40 years data)
Table 42 - currency with public, demand and time deposits, reserve money and others (60 years data)
Table 44 - rates and ratios (repo rate, bank rate, SLR, CRR, MSF and others) - date-wise changes from 2005 to 2023
Table 49 - Banks (maturity pattern of deposits)
Table 54 - NPAs of banks
Table 63 - structure interest rates (break-up of year-wise deposit interest rates and lending rates)
Table 64 - flow of resources to commercial sector
Table 74 - AUM of mutual funds (16 years data)
Table 91 - BSE market cap (30 years data)
Table 92 - key deficit indicators of gov't - fiscal deficit, revenue deficit, etc (40 years data)
Table 108 - government market borrowings
Table 110 - outstanding laibilities of central government
Table 113 - ownership pattern of G-Secs (as owned by banks, insurance companies, mutual funds, provident funds, RBI, etc.)
Table 114 - small savings schemes (interest rates)
Table 115 - small savings (receipts and outstandings) (40 years data)
Table 117 - India exports and imports
Table 121 - imports of principal commodities (including crude oil)
Table 123 - exports of select commodities (country-wise)
Table 130 - balance of payments (BoP)
Table 138 - exchanges rates of INR vs USD, euro, etc. (40 years data)
Table 140 - NEER and REER
Table 145 - NRI deposits
Table 149 - FDI and FPI flows (22 years data)
Table 150 - forex reserves (almost 60 years data)
Table 151 - external debt to GDP ratio, short term debt ratio, etc. (18 years data)
Tables below provide quarterly / monthly series data:
Table 164 - WPI (monthly data for 7 years)
Table 165 - CPI (monthly data for 5 years)
Table 176 - weighted average call money rates (5 years data)
Table 177 - RBI's open market operations (OMO) (4 years data)
Tables below provide annual data for several years (often more than 20 years data):
Table 226 - growth rates of reserve money, currency with public, demand deposits, time deposits and others (36 years data)
Table 227 - growth rates of demand and time deposits, investment in G-Secs, bank credit and others (55 years data)
Table 228 - banks - CD ratio, G-sec to deposits ratio, credit to GDP ratio, deposits to GDP ratio, etc. (60 years data)
Table 230 - WPI percentage changes (40 years data)
Table 232 - select government fiscal indicators as a % of GDP - like, fiscal deficit, revenue deficit, tax to GDP ratio, etc. (more than 40 years data)
Table 234 - combined fiscal and revenue deficits of centre and states as a % of GDP (almost 40 years data)
Table 235 - balance of payments or BoP indicators - like, exports to GDP ratio, imports to GDP ratio, CAD to GDP ratio, net FDI to GDP ratio, net FPI to GDP ratio, import cover and others (almost 40 years data)
Table 238 - CPI (month-wise annual variation)
Table 239 - Sensex P/E ratio
Table 240 - Sensex P/B ratio
Those who are interested in research may find both the Annual Report and Handbook of Statistics on Indian Economy very useful.
(While uploading the blog, some portions of the blog were inadvertently removed without my intervention. Hence, the missed portions were reconstructed from memory and it was finished the next morning).
- - -
------------------------------
References:
------------------------------Read more:
Disclosure: I've vested interested
in Indian stocks and other investments. It's safe to assume I've interest in the financial instruments / products discussed, if
any.
Disclaimer: The analysis and
opinion provided here are only for information purposes and should not be construed
as investment advice. Investors should consult their own financial advisers
before making any investments. The author is a CFA Charterholder with a vested
interest in financial markets.
CFA Charter credentials - CFA Member Profile
CFA Badge
He blogs at:
https://ramakrishnavadlamudi.blogspot.com/
https://www.scribd.com/vrk100
X (Twitter) @vrk100